WikiDevi.Wi-Cat.RU:DD-WRT/DNSMasq as DHCP server
DD-WRT supports using DNSMasq as a local DNS server and can also support using replacement of the standard DD-WRT DHCP service "udhcpd". uDHCPd uses more RAM than DNSMasq.
Using DNSMasq as the sole DHCP server can save you 300kB. With this savings you can create one more PPTP tunnels with the inserted PPTPD server.
An added advantage is that DNSMasq can intelligently add DHCP leases to its DNS database, providing local name lookups for any DHCP client, static or dynamic.
udhcpd, a DHCP server (daemon), is not to be confused with udhcpc, the DHCP client. Most setups require that the router run udhcpc to acquire DHCP leases for the WAN interface.
There are two ways to configure DNSMasq to become the dhcp server.
- Using the Web-Interface (most options are configurable here)
- Using DNSMasq parameters (for advanced users who can understand dnsmasq.conf file layout, and know where to find the manual page for it)
You can NOT use both
Configuration
Using Web-Admin
This is the easiest way to setup DNSMasq as DHCP Server
- Go to your Web-Interface and log in
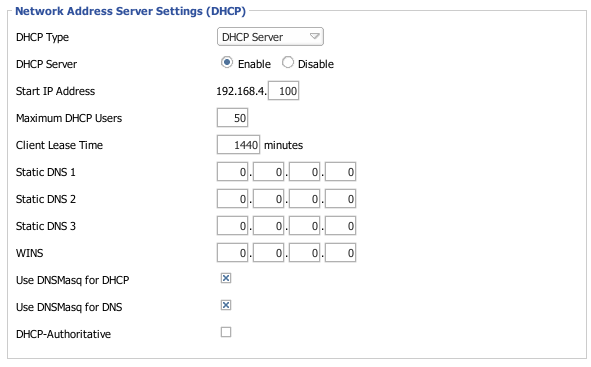
- Go to Setup->Basic Setup
- Make sure that
- DHCP Type = DHCP Server
- DHCP Server = Enable
- Use DNSMasq for DHCP = Checked
- Use DNSMasq for DNS = Checked
- Make sure that
Make sure that the maximum number of DHCP leases that you set is appropriate for your netmask; otherwise, DNSMasq will not start.
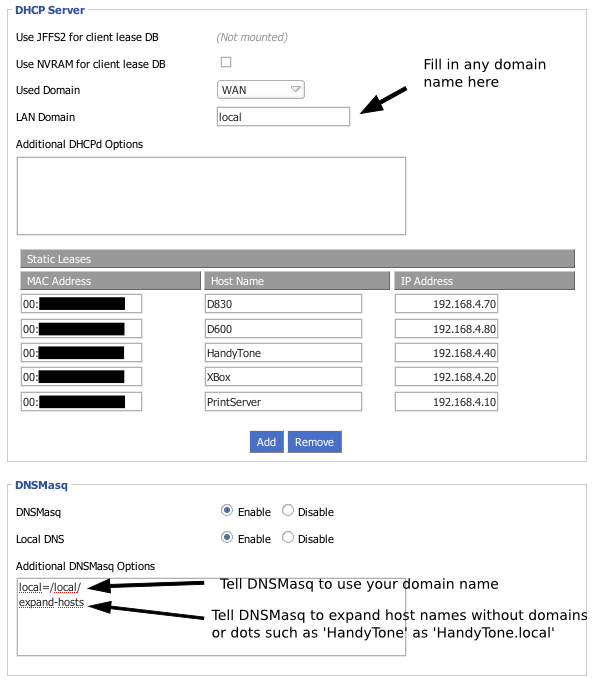
- Go to Administration->Services
- Make sure that
- LAN Domain = <chosen LAN domain>
- DNSMasq = Enabled
- Local DNS = Enabled
- Additional DNSMasq Options = Add your domain as a local search domain, add expand-hosts option. See screenshot.
- Make sure that
- You can add static allocations the same way as when you're using DHCPd. These settings should end up in /tmp/dnsmasq.conf.
Update: For DNSMasq Options, I found the explanation below confusing; it's much simpler than it sounds. Assuming your LAN domain is called 'lan', put the following lines in the "additional DNSMasq options" field:
domain=lan local=/lan/ expand-hosts
--Mjrpes 07:53, 31 August 2010 (CEST)
In the below screenshot, there are a couple of mistakes. In order for expand-hosts to work, you need a domain=local line in there as well. But "local" is not a good idea for a local domain, because multicast / ZeroConf uses ".local" for its own purposes. You can get strange results like nslookup working while pings fail. Pick something other than ".local" for your domain.
--Towelie 15:57, 23 November 2010 (CEST)
For me (with WRT350N-15508std) the above description didn't work (could resolve names in LAN only - you may check my topic). The problem is: If you use DNSMasq as DHCP Server the LAN Domain is already written into DNSMasq conf and if you add it to Additional DNSMasq Options it's been added twice and (quoting frater:) the thing goes berserk. So the cleanest solution is setting Used Domain to LAN/WLAN and don't add the domain-entry into Additional DNSMasq Options.
Use NVRAM for client lease DB enabled DNSmasq does not start, did not check log for error, disable it operates correctly. Incorrect addition of DHCP maximum number of users and number of reservations within the scope; i.e: 25 max + 5 reservations within scope yields 30 user max and if it is at the high end of the subnet it will push the upper boundary of addresses outside of limit and DHCP will not run. WRT54GSv5 Firmware: DD-WRT v24-sp1 (07/27/08) micro
DNSMasq DHCP Parameters
As of v24, DNSMasq respects the settings of the DHCP server on the "Setup" page and static leases set on the "Services" page
Option 66 for TFTP
If would like to use a DHCP support for TFTP (TFTP Server Address) server
dhcp-option=66,"192.168.1.100"
were 192.168.1.100 is address of tftp server You need use quotes around server address in option 66
(this otion is needed if you use cisco IP phone systems to configure.
Old Way
This provides access to more functionality at the expense of not being able to use the structured web interface.
Following steps are necessary:
- Deactivate the DHCPD service on the "Setup" page.
[Comment: above step deactivated all DHCP for me and wasn't needed anyway - andmalc 4/2008]
- Under the "Administration" tab in the "Services" sub tab, you will find a "DNSMasq" section. Under "Additional DNS Options", you need to set some parameters.
* To setup the default options for Dynamic IP Allocation, add: dhcp-range=192.168.1.100,192.168.1.150,255.255.255.0,24h
* To setup machines to have a Static IP assigned by the router, add either: dhcp-host=AB:CD:EF:11:22:33,192.168.1.10,24h or dhcp-host=computername,192.168.1.10,24h
AB:CD:EF:11:22:33 is the MAC of the network, computername is the NetBIOS name of the computer on the network, 192.168.1.10 indicates the desired IP, and finally 24h the DHCP lease of 24 hours, however if you wish to have the lease for the machine never expire, you may do so by changing 24h to infinite.
If it's not possible to assign an IP with DNSMasq and you want to identify devices via name resolution, you must add the following lines:
no-hosts addn-hosts=/tmp/hosts
You must also add this computer to /tmp/hosts:
192.168.0.5 printers drucker.lan
[Comment: In v23-SP2 (and possibly other versions) /etc/hosts is simply a softlink to /tmp/hosts. To get the last part to work you need to remove the no-hosts part and specify a separate hosts file for the static assignments. --Wishyou 22:57, 19 June 2008 (CEST) ]
Extra DNSMasq options
There are some extra options in the web interface for DNSMasq that you can set by entering them in Additional DNSMasq Options on the "Services" tab.
ISP DNS-Servers
If you wish to pass through the DNS servers from your ISP, you can use the following parameters:
dhcp-option=6, x.x.x.x, y.y.y.y where x.x.x.x = DNS1 y.y.y.y = DNS2
DNS Preferred Order
If you want to use DNS servers in a so-called "strict order" of operation, add this to the DnsMasq Box
strict-order
Assign an alternate Gateway
By default, dd-wrt will hand out via DHCP its own IP as the Gateway. You can specify an alternate one like so:
dhcp-option=3,x.y.z.w
A related but different solution is to create a DHCP setting that gives a static IP address to a certain MAC, but with a different Gateway address than the rest.
dhcp-range=net:2,172.16.51.0,255.255.255.0,static dhcp-option=net:2,3,172.16.51.2
Then use:
dhcp-host=<hwaddr>, net:2, <ipaddr>
click here for more details...
Static Route
Instead of having a default router set up on the router, you can push a static route to client computers. This is useful, for instance, if you have a VPN server that is NOT the DD-WRT router. This will offload the router from having to redirect packets to the correct destination and will take one hop off the traffic path.
***Remember that the static route will not show up on the client computers UNTIL they request a new ip***
To accomplish this, we use DHCP option 121 (which replaced option 33) and allows you to use the netmask:
dhcp-option=121,x.x.x.x/yy,z.z.z.z
Where x.x.x.x is the destination LAN, yy is the CIDR notation (usually /24), and z.z.z.z is the host which will do the routing.
Denying DHCP service to specific MAC addresses
You can ignore requests from specific MAC addresses, so that no IP address will be leased to those specific MAC addresses/machines
dhcp-host=11:22:33:44:55:66,ignore 11:22:33:44:55:66 = MAC address of the machine you wish to ignore
Enable TFTP server
You can start a tftp server serving files from "/opt/tftpboot". This may prove useful for upgrading firmwares for embedded devices. Due to space constraints this feature is currently not supported. Use the optware package instead and disable the built-in dnsmasq service.
enable-tftp tftp-root=/opt/tftpboot
Disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP
Since DNSMasq acting as a local DNS server suitably takes care of host name resolution, disabling NetBT on appropriately configured Microsoft DHCP clients, such as Windows 2000 and XP, can be accomplished with the following:
dhcp-option=43,01:04:00:00:00:02
Troubleshooting
It's possible to verify that the options you set in the web interface match those being passed to DNSMasq. telnet to your router's IP address and log in as root with your usual password. Then:
cat /tmp/dnsmasq.conf
The options should match the command-line format specified in the DNSMasq man page.
You should also make sure that DNSMasq is running at all. To do so, while in telnet issue
/bin/ps | grep [d]nsmasq
The output should look like:
144 root 772 S dnsmasq --conf-file=/tmp/dnsmasq.conf
If the line is missing, DNSMasq isn't running and may have been unable to start due to one of its options being set incorrectly.
To find out why DNSmasq is failing; you can find out what the error return code is by issuing DNSmasq from the command line:
# dnsmasq -t --conf-file=/tmp/dnsmasq # echo $? 1 #
Most likely it's RC=1 and that means something is wrong with the config file. It could be something as simple as having the same command twice in the config file, to have DNSmasq fail.
EXIT CODES
0 - DNSmasq successfully forked into the background, or terminated normally if backgrounding is not enabled.
1 - A problem with configuration was detected.
2 - A problem with network access occurred (address in use, attempt to use privileged ports without permission).
3 - A problem occurred with a file system operation (missing file/directory, permissions).
4 - Memory allocation failure.
5 - Other miscellaneous problem.
11 or greater - a non zero return code was received from the lease-script process "init" call. The exit code from DNSmasq is the script's exit code with 10 added.
External Links
http://www.faqs.org/rfcs/rfc2132.html Options on MAC addresses
http://www.iana.org/assignments/bootp-dhcp-parameters/bootp-dhcp-parameters.xml DHCP Option Parameters