List of Single-board microcontrollers
Comparison of Single-board microcontrollers
- excluding Single-board computers.
• Comparison of single-board microcontrollers on Wikipedia
Arduino
| Name | Maker | Processor | Format | Host interface | Memory | In/Out (pins) | Release date | Notes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Manuf | CPU / MCU (WLAN) |
Freq. | Form factor |
Dimensions | IF | Host | Voltage (V) | Flash (kB) | EEPROM (kB) | RAM (kB) | Digital I/O |
Digital w/PWM |
Analog In/(Out) |
(Announce) | (Images) |
| Arduino / Genuino MKR1000 |
Arduino | Atmel ATSAMW25 SAMD21 MCU 32bit ARM (Cortex-M0+), WINC1500 802.11b/g/n, and ECC508 crypto device |
48MHz | minimal | 61.5 × 25 mm | USB | 3.3 V | 256 | No | 32 | 8 | 12 | 7 (1) | Announced: April 2, 2016 | ||
| Arduino 101 [1] Genuino |
Arduino | Intel Curie module [2] two tiny cores, an x86 (Intel Quark SE) and an ARC |
32MHz | Arduino / Genuino | 68.6 × 53.4 mm | USB | 3.3 V | 196 | 24 | 14 | 4 | 6 | October 16, 2015 | Contains six-axis accelerometer, gyroscope and bluetooth | ||
| Arduino Zero [3] | Arduino | Atmel ATSAMD21 G18A [4] |
48MHz | Arduino | 68.6 × 53.3 mm | USB | Native & EDBG Debug | 3.3 V | 256 | 0 to 16Kb emulation | 32 | 14 | 12 | 6 | Released: June 15, 2015 [5] Announced: May 15, 2014 [6] Listed on some vendors list Mar, 2015 |
Beta testing since Aug 1, 2014 [7] |
| Arduino Due [8] [9] | Arduino | Atmel ATSAM3 X8E [10] ARM (Cortex-M3) |
84MHz | Mega | 4 in × 2.1 in [ 101.6 mm × 53.3 mm ] | USB | 16U2 [11] + native host [12] | 3.3 V | 512 | 0 [13] | 96 | 54 | 12 | 12 (2) | October 22, 2012 [14] | The first Arduino board based on an ARM Processor. Features 2 channel 12-bit DAC, 84MHz clock frequency, 32-bit architecture, 512KB Flash and 96KB SRAM. Unlike most Arduino boards, it operates on 3.3V and is not 5V tolerant. |
| Arduino Yún [15] Arduino Yún Rev 2 |
Arduino . SeeedStudio |
Atmega32U4 [16] Atheros AR9331 |
16MHz . 400MHz |
Arduino | 2.7 in × 2.1 in [ 68.6 mm × 53.3 mm ] | USB | 5 V | 32 kB . 16 MB |
1 kB, 0 kB |
2.5 kB . 64 MB |
14 | 6 | 12 | September 10, 2013 [17] | Arduino Yún is the combination of a classic Arduino Leonardo (based on the Atmega32U4 processor) with a Wi-Fi SoC running Linino, a MIPS GNU/Linux based on OpenWrt. | |
| Arduino Leonardo [18] | Arduino | Atmega32U4 [16] | 16MHz | Arduino | 2.7 in × 2.1 in [ 68.6 mm × 53.3 mm ] | USB | 32U4 [16] | 5 V | 32 | 1 | 2.5 | 20 | 7 | 12 | July 23, 2012 [19] | The Leonardo uses the Atmega32U4 processor, which has a USB controller built-in, eliminating one chip as compared to previous Arduinos. |
| Arduino Uno [20] | Arduino | ATmega328P [21] | 16MHz | Arduino | 2.7 in × 2.1 in [ 68.6 mm × 53.3 mm ] | USB | 8U2 [22] (Rev1&2) / 16U2 [11] (Rev3) |
5 V | 32 | 1 | 2 | 14 | 6 | 6 | September 24, 2010 [23] | This uses the same ATmega328 as late-model Duemilanove, but whereas the Duemilanove used an FTDI chip for USB, the Uno uses an ATmega16U2 (ATmega8U2 before rev3) programmed as a serial converter. |
| Arduino Mega 2560 [24] | Arduino | ATmega2560 [25] | 16MHz | Mega | 4 in × 2.1 in [ 101.6 mm × 53.3 mm ] | USB | 8U2 [22] (Rev1&2) / 16U2 [11] (Rev3) |
5 V | 256 | 4 | 8 | 54 | 15 | 16 | September 24, 2010 [23] | Total memory of 256kB. Uses the ATmega16U2 (ATmega8U2 before Rev3) USB chip. Most shields that were designed for the Duemilanove, Diecimila, or Uno will fit, but a few shields will not fit because of interference with the extra pins. |
| Arduino Ethernet [26] | Arduino | ATmega328 [27] | 16MHz | Arduino | 2.7 in × 2.1 in [ 68.6 mm × 53.3 mm ] | Ethernet Serial interface | Wiznet Ethernet | 5 V | 32 | 1 | 2 | 14 | 4 | 6 | July 13, 2011 [28] | Based on the same WIZnet W5100 chip as the Arduino Ethernet Shield. [29] A serial interface is provided for programming, but no USB interface. Late versions of this board support PoE. |
| Arduino Fio [30] | Arduino | ATmega328P [21] | 8MHz | minimal | 2.6 in × 1.1 in [ 66.0 mm × 27.9 mm ] | XBee Serial | 3.3 V | 32 | 1 | 2 | 14 | 6 | 8 | March 18, 2010 [31] | Includes XBee socket on bottom of board. [30] | |
| Arduino Nano [32] | Arduino | ATmega328 [27] (ATmega168 before v3.0 [33]) |
16MHz | minimal | 1.7 in × 0.7 in [ 43.2 mm × 17.8 mm ] | USB | FTDI FT232R [34] | 5 V | 16/32 | 0.5/1 | 1/2 | 14 | 6 | 8 | May 15, 2008 [35] | This small USB-powered version of the Arduino uses a surface-mounted processor. |
| Arduino LilyPad [36] | Arduino | ATmega168V or ATmega328V | 8MHz | wearable | 2 in [ 51 mm ] | 2.7-5.5 V | 16 | 0.5 | 1 | 14 | 6 | 6 | October 17, 2007 [37] | This minimalist design is for wearable applications. | ||
| Arduino Pro [38] | Arduino | ATmega168 or ATmega328[38] | 16MHz | Arduino | 2.0 in × 2.1 in [ 50.8 mm × 53.3 mm ] | UART, Serial, I2C (TWI), SPI | FTDI | 5 V or 3.3 V | 16/32 | 0.5/1 | 1/2 | 14 | 6 | 6 | Designed and manufactured by SparkFun Electronics for use in semi-permanent installations. | |
| Arduino Mega ADK [39] | Arduino | ATmega2560 [25] | 16MHz | Mega | 4 in × 2.1 in [ 101.6 mm × 53.3 mm ] | 8U2 [22] MAX3421E USB Host |
5 V | 256 | 4 | 8 | 54 | 14 | 16 | July 13, 2011 [28] | ||
| Arduino Esplora [40] | Arduino | Atmega32U4 [16] | 16MHz | 6.5 in × 2.4 in [ 165.1 mm × 61.0 mm ] | 32U4 [16] | 5 V | 32 | 1 | 2.5 | December 10, 2012 | Analog joystick, four buttons, several sensors, 2 Tinker Kit inputs and 2 outputs, LCD connector | |||||
| Arduino Micro [41] | Arduino | ATmega32U4 [16] | 16MHz | Mini | 0.7 in × 1.9 in [ 17.8 mm × 48.3 mm ] | 5 V | 32 | 1 | 2.5 | 20 | 7 | 12 | November 8, 2012 [42] | This Arduino was co-designed by Adafruit. | ||
| Arduino Pro Mini | Arduino | ATmega328 | 8MHz (3.3V) / 16MHz (5V) |
Mini | 0.7 in × 1.3 in [ 17.8 mm × 33.0 mm ] | Six pin serial header | 3.3 V / 5 V | 32 | 1 | 2 | 14 | 6 | 6 | Designed and manufactured by SparkFun Electronics. | ||
| Arduino Serial [43] | Arduino | ATmega8 [44] | 16MHz | Arduino | 3.2 in × 2.1 in [ 81.3 mm × 53.3 mm ] | DE-9 serial connection | native | The first board labelled "Arduino". | ||||||||
| Arduino USB [45] | Arduino | ATmega8 [44] | 16MHz | Arduino | 3.2 in × 2.1 in [ 81.3 mm × 53.3 mm ] | USB | FTDI FT232BM | Changed: USB replaces RS-232 interface, Improved: Arduino can be powered from host. | ||||||||
| Arduino Extreme [45] | Arduino | ATmega8 [44] | 16MHz | Arduino | 3.2 in × 2.1 in [ 81.3 mm × 53.3 mm ] | USB | The Arduino Extreme uses many more surface mount components than previous USB Arduino boards and comes with female pin headers. [45] | |||||||||
| Arduino NG (Nuova Generazione) [45] |
Arduino | ATmega8 [44] | 16MHz | Arduino | 3.2 in × 2.1 in [ 81.3 mm × 53.3 mm ] | USB | FTDI FT232RL | Improved: FT232BM has been replaced by FT232RL to require fewer external components, LED on pin 13 added. | ||||||||
| Arduino NG plus | Arduino | ATmega168 [33] | 16MHz | Arduino | 3.2 in × 2.1 in [ 81.3 mm × 53.3 mm ] | USB | ||||||||||
| Arduino BT (Bluetooth) [46] |
Arduino | ATmega168 [33] ATmega328 [27] |
16MHz | Arduino | 3.2 in × 2.1 in [ 81.3 mm × 53.3 mm ] | Bluetooth | BlueGiga WT11 Bluetooth | 5 V | 32 | 1 | 2 | 14 | 4 | 6 | October 22, 2007 [47] | Similar to the Arduino NG, this has a Bluetooth module rather than a serial interface. [46] Programming is carried out via Bluetooth. |
| Arduino Diecimila [48] | Arduino | ATmega168 (DIP-28) [33] |
16MHz | Arduino | 2.7 in × 2.1 in [ 68.6 mm × 53.3 mm ] | USB | FTDI | 5 V | 16 | 0.5 | 1 | 14 | 6 | 6 | October 22, 2007 [47] | Improved: Host is able to reset the Arduino, pin headers for reset and 3.3V, low dropout voltage regulator allows lower voltage on external power source. |
| Arduino Duemilanove (2009) [49] |
Arduino | ATmega168, [33] ATmega328P (ATmega328 for newer version) |
16MHz | Arduino | 2.7 in × 2.1 in [ 68.6 mm × 53.3 mm ] | USB | FTDI | 5 V | 16/32 | 0.5/1 | 1/2 | 14 | 6 | 6 | October 19, 2008 [50] | Improved: automatically switching between USB and external power, eliminating jumper. |
| Arduino Mega [51] | Arduino | ATmega1280 [52] | 16MHz | Mega | 4 in × 2.1 in [ 101.6 mm × 53.3 mm ] | USB | FTDI | 5 V | 128 | 4 | 8 | 54 | 14 | 16 | March 26, 2009 [53] | Uses a surface-mounted ATmega1280 for additional I/O and memory. [54] |
| Arduino Mini [55] | Arduino | ATmega168 [33] (Pro uses ATMega328) |
8MHz (3.3V)/ 16MHz (5V) |
0.7 in × 1.3 in [ 17.8 mm × 33.0 mm ] | 5 | 16 | 0.5 | 1 | 14 | 6 | 6 | August 23, 2008 [56] | This miniature version of the Arduino uses a surface-mounted processor. | |||
Other
| Name | Maker | Processor | Format | Host | Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Manuf | Processor | Freq. | Form. | Dim. | IF | Volt. | |
| Canaduino Uno Bone | Universal Solder | Atmega 328P-PU |
16MHz | Do-It-Yourself Arduino Uno R3 compatible footprint and connections. Additional features:
| ||||
| ST1 | Sanjay Technologies [57] | ATmega 328 |
Compatible With Arduino Uno Rev3 - Added features:
| |||||
| ST Freeduino Robotics Board |
Sanjay Technologies [58] | ATmega 328 |
Compatible With Arduino with servo ports - Added features:
| |||||
| GSTduino | Green System Technology [59] | ATmega 328 |
16MHz | 55x45mm | Added features:
| |||
| Linduino One | Linear Technology | ATmega 328 |
Compatible with Arduino Uno. Galvanically isolated USB interface provided by onboard LTM2884 USB Isolation module. | |||||
| InVentor UNO | Ventor Technologies | ATmega 328P-PU |
16MHz | Added Features:
| ||||
| InvIoT U1 | InvIoT.com | ATmega 328P-PU |
16MHz | 140x65mm |  All-in-one board with LCD, rotary encoder, RTC DS3231, EEPROM,
| |||
| Bluno | DFRobot.com | ATmega 328 |
Added Features:
| |||||
| AVR.duino U+ | SlicMicro.com | ATmega 328 |
 Compatible With Arduino Uno Rev3
| |||||
| SainSmart UNO [60] | SainSmart [61] | ATmega 328 |

| |||||
| SainSmart UNO R3 [62] | SainSmart [61] | ATmega 328-AU |
 Development board compatible with Arduino Uno Rev3
| |||||
| SainSmart Mega 2560 [63] | SainSmart [61] | ATmega 2560 [25] |

| |||||
| Freaduino MEGA2560 | ElecFreaks | ATmega 2560 [25] |
| |||||
| AVR-Duino [64] | TavIR [65] | Another Arduino/Mega compatible board. | ||||||
| Brasuíno [66] | Holoscópio [67] | 
| ||||||
| ChibiDuino2 [68] | TiisaiDipJp [68] | ATmega 328 |
| |||||
| Cosmo Black Star [69] | JT5 [70] | ATmega 328 |
Arduino layout-compatible board. Based on the Arduino Duemilanove. | |||||
| CraftDuino [71] | RoboCraft Team | - | ||||||
| CT UNO | Cytron Technologies | ATmega 328P |
CT-UNO Features:
| |||||
| CT ARM (ARM Cortex M0)] |
Cytron Technologies | NUC131 LD2AE 32-bit ARM (Cortex-M0) |
50MHz | Arduino | 69×53mm | CT-ARM Features:
| ||
| Diavolino [72] | Evil Mad Scientist Lab |
 Arduino layout-compatible board, designed
| ||||||
| DuinoBot v1.x [73] | RobotGroup Argentina [74] | ATmega 32U4 |
Arduino fully compatible board, with integrated
| |||||
| eJackino [75] | Kit by CQ publisher in Japan | Similar to Seeeduino, eJackino can use
On back side, there is a "Akihabara station"
| ||||||
| gizDuino v5.0V | e-gizmo | Atmega168, Atmega328 |
*Arduino Compatible
| |||||
| Elektor Platino Universal AVR board [76] |
Elektor | ATmega8, ATmega16, ATmega32, ATmega88, ATmega164, ATmega168, ATmega324, ATmega328, ATmega644, ATmega1284 |
Platino is an Arduino compatible board that supports 28-pin and 40-pin AVR devices.
On its backside are Arduino shield compatible connectors
| |||||
| Fayaduino series [77] | Fayalab [78] | - | ||||||
| Freeduino MaxSerial [77] | Fundamental Logic |
A board with a standard DE-9 serial port. | ||||||
| Freeduino SB [79] | Solarbotics Ltd. [80] | ATmega 328 |
 Compatible with the Duemilanove. | |||||
| Freeduino Through-Hole [81] | NKC Electronics | The design avoids surface-mount soldering. | ||||||
| Illuminato Genesis [82] | ATmega 644 |
Provides 64kB of flash, 4kB of RAM and 42x general I/O pins.
| ||||||
| InduinoX [83] | Simple Labs [84] | ATmega168, ATmega 328, ATmega 8 |
A low cost Arduino clone using the ATmega 8/168/328 and designed for prototyping,
| |||||
| Japanino [85] | Otonano Kagaku | ATmega 168 [33] |
The board and a POV kit were included in Vol.27 of the eponymous series.
| |||||
| 1000Pads Luigino [86] | Minimalistic version of Arduino: small, without serial converter.
Smaller than Arduino, with different footprint. | |||||||
| Luigino328 [87] | ATmega 328 |
It has an improved automatic voltage selector, resolves problems during programming caused by shields
| ||||||
| Metaboard [88] | Metalab | Designed to have a very low complexity and price.
| ||||||
| Rascal | Rascal Micro [89] | AT91SAM 9G20 (ARM9) |
It is compatible with Arduino shields, but it is programmed
| |||||
| Raspduino [90] | Bitwizard [91] | ATmega 328 |
Fully Arduino compatible board, that fits perfectly on a Raspberry Pi,
It also breaks out the Raspberry Pi's SPI and I²C interfaces, or can be
| |||||
| Romeo 2012 [92] | DFRobot [93] | ATmega 328 |
 An all-in-one Arduino with motor controller.
| |||||
| Roboduino [94] | Curious Inventor | 
| ||||||
| Seeeduino [95] | SeeedStudio | v2.21 (Atmega168 or Atmega328) v3.0 (Atmega328) |

| |||||
| SunDuino [96] | Lothar Team | ATmega 8/88/168/328/ 16/32/324/644 and PIC18F2550/4550 PIC32MX320F128 and ButterFLY, STM32 Discovery |
Another Arduino compatible board, software- and hardware-compatible. | |||||
| TwentyTen [97] | Freetronics [98] | 
| ||||||
| UDOO Category:UDOO |
SECO Inc. | Atmel SAM3X8E |
250px Android-Linux-Arduino compatible board. | |||||
| Volksduino [99] | Applied Platonics [100] | *A low cost, high power, shield-compatible, complete Arduino-
| ||||||
| Wiseduino [101] | *Includes a DS1307 RTC with backup battery, a 24LC256 EEPROM
| |||||||
| Xaduino | OBDII world | ATXmega 128A3U |
32MHz | *8/16-bit Xmega core @32MHz
| ||||
| YourDuino RoboRED | Yourduino.com [102] | Atmel 328 |
250px
| |||||
| YourDuino Robo1 [103] | Yourduino.com [102] | Atmel 328 |
*Includes 6 color-coded 3-pin connectors for direct cable connection
| |||||
| ZArdino [104] | A kit created by Peter Ing | ATMega 328 |
*A South African Arduino-compatible board derived from the Duemilanove, it features mostly
| |||||
| Zigduino [105] | Logos Electro- mechanical [106] |
ATmega 128RFA1 |

| |||||
| EtherTen [107] | Freetronics | ATmega 328P |
*Fixed SPI behaviour on Ethernet chip, D13 pin isolated
| |||||
| EtherMega [108] | Freetronics | ATmega 2560 [25] |
*Fixed SPI behaviour on Ethernet chip, Micro SD card slot, D13 pin
| |||||
| USB Droid [109] | Freetronics | ATmega 328P |
Can act as a host for an Android device and is compatible with the Android Open Accessory Development Kit,
| |||||
| Eleven [110] | Freetronics | ATmega 328P |
Arduino Uno compatible, D13 pin isolated with a MOSFET of which can also be used as an input. | |||||
| KitTen [111] | Freetronics | ATmega 328P |
Includes both 3.3V and 5V regulators for shields, D13 pin isolated with a MOSFET of which can also be used as an input.
| |||||
| EtherDue [113] | Freetronics | ATSAM3X8E [10] ARM (Cortex-M3) |
Arduino Due with onboard Ethernet, software-compatible with Arduino Ethernet Shield,
| |||||
| TAIJIUINO Due Pro [114] | Elechouse | ATSAM3X8E [10] (Cortex-M3) | Mostly compatible with Arduino Due. Includes RMII signals via a connector
| |||||
| ShieldBuddy TC275 [115] | Hitex UK | Infineon Aurix TC275TP |
200MHz | Uses Arduino Due form factor and largely compatible pin allocation.
| ||||
| MBZ Pro WiFi | MaxBlitz | Atmega 328P-PU |
 MBZ Pro Mega is an Arduino compatible stand-alone
Featuring a compact design, it helps to shrink
| |||||
| Io:duino [116] | Railstars | AT90CAN128 | USB w/ FTDI serial chip |
*Adds built-in CAN bus support through the AT90CAN128 micro processor, dual RJ45 jacks,
| ||||
| DFRobotShop Rover [117] | ATmega 328 |
This is a minimalist tracked platform based on the Arduino Duemilanove. Has an ATmega328 with Arduino bootloader, a dual H-bridge and additional prototyping space and headers. It is compatible with many shields, though four digital pins are used when operating the motor controller. Has an onboard voltage regulator, additional LEDs, a temperature sensor, and a light sensor. Part of the DFRobotShop Rover kit. | ||||||
| Faraduino [118] | Developed by Middlesex University Teaching Resources [119] |
ATmega 328 |
USB w/ FTDI serial chip |
 Simple shield-compatible board, with onboard discrete transistor H-bridges and screw terminals to drive two small DC motors from pins 4–7. [120] Has headers for three servos on pins 9-11. | ||||
| Motoruino [123] | Guibot | ATmega 328 |
Serial only, 6-pin header |
 Has L293D twin H-bridge. | ||||
| Alternator Regulator [124] |
ATmega 64M1 |
USB w/ FTDI serial chip |
*Open source Alternator Regulator suitable for 12v to 48v systems with many different battery chemistries (Lead-Acid, LiFeP04, etc..).
| |||||
| ArduPilot [125] | 
| |||||||
| ArduIMU [125] | *An Arduino-compatible board designed for Inertial Measurement
| |||||||
| FlyDuino Mega [126] | Paul Bake | ATmega 2560 [25] |
Serial only, 6-pin header |
*An Arduino Mega 2560 compatible board designed for auto-piloting
| ||||
| Colibri [127] | JT5 [70] | ATmega 168 [33] |
Serial only | *Universal Platform for Wireless Data Transmission in the Frequency Band 868MHz.
| ||||
| JeeNode | Jeelabs | ATmega 328 |
6-pin header | *Includes a wireless radio module, called the RFM12B by HopeRF | ||||
| ArduPhone [128] | Freetronics | ATmega 1284P |
USB | *Cellular phone kit, ADH8066 GSM module,
| ||||
| WTFDUINO [129] | Calum Knott | ATmega 328p |
USB & CH340G | "The world needs a more confusing Arduino" | ||||
| Tah [130] | Revealing Hour Creations [131] | ATmega 32u4 |
USB | *Stock Arduino Leonardo with a built-in BT BLE 4.0. Has arduino compatibility with its breakout shield. | ||||
| WIOT | ubld.it | ATmega 32u4 |
USB | 
| ||||
| XLR8 | Alorium Technology | Altera MAX10 10M08 FPGA |
USB | *FPGA-based drop-in replacement for Arduino UNO R3; offers faster clock rates and overall applications speed,
| ||||
| Controllino Mini [132] | Controllino | ATmega 328 |
USB | 12/24V | *8x Analog/Digital Inputs, 6x Relays Outputs, 8x Digital Outputs
| |||
| Controllino Maxi [132] | Controllino | ATmega 2560 |
Ethernet / USB |
12/24V | *12x Analog/Digital Inputs, 10x Relays Outputs, 12x Digital Outputs
| |||
| Controllino Mega [132] | Controllino | ATmega 2560 |
Ethernet / USB |
12/24V | *12x Analog/Digital Inputs, 10x Relays Outputs, 12x Digital Outputs
| |||
| FA-DUINO 12RA [133] | Comfile Technology |
Mega 2560 |
RS232 | 24V | *8x Inputs, 4x Relays | |||
| FA-DUINO 24RA | Mega 2560 |
RS232 | 24V | *16x Inputs, 8x Relays | ||||
| ARDBOX [134] | Industrial Shields |
Atmega 32U4 |
USB | 12/24V | *10x Input, 10x Output
| |||
| Industruino [135] | Industruino | Atmega32u4 or AT90USB1286 |
USB | 6/32V | *8x shared digital Input/Output, 4x Analog input, 2 Analog output
| |||
| Iono [136] | Sfera Labs | No integral board | USB / 6-pin header |
11/30V | 6x Input, 6x Output
| |||
| Ardweeny [137] | Solarbotics | An inexpensive, even more compact breadboardable device. | ||||||
| Banguino [138] | Dimitech | ATmega 328 |

| |||||
| SAM15x15 | avdweb | SAMD21G18 |  Mini SAMD21 development board 15x15mm (Arduino compatible)
| |||||
BBB
| Name | Maker | Processor | Format | Host | Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Manuf | Processor | Freq. | Form. | Dim. | IF | Volt. | |
| Bare Bones Board (BBB) and Really Bare Bones Board (RBBB) |
Modern Device | Compact inexpensive Arduino-compatible board suitable for breadboarding. | ||||||
| BBFUINO (Breadboard Friendly Arduino Compatible) |
Cytron Technologies |
ATmega328P | BBFuino come with the ATMega328 controller, loaded with Optiboot (Arduino UNO's bootloader), compatible with Arduino IDE and sample code, design to fit breadboard for prototyping and learning, lower down the cost by taking out the USB to UART IC, so the board has the basic component to operate. | |||||
| BlockDuino [139] | Blockduino | ATmega8 ATmega328 |
An Arduino-Diecimila-compatible board with serial connection to Blocks (shields). [140] | |||||
| Boarduino [141] | Adafruit | ATmega168 or ATmega328 |
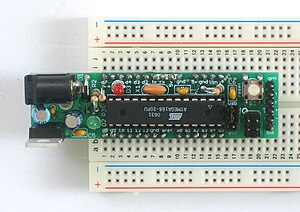 An inexpensive Arduino-Diecimila-compatible board made for breadboarding. | |||||
| Breaduino [142] | Applied Platonics [100] |
A complete, very low cost Arduino-compatible kit that can be assembled entirely on a breadboard. | ||||||
| Croduino series [143] | e-radionica.com | ATmega328 | Inexpensive series of fully compatible Arduino board for education, hobbyist and automatisation, specially in Croatia. | |||||
| Cardboarduino [144] | ATmega168 [33] | Inspired by the Paperduino, an ultra low-cost Arduino compatible, built on printed posterboard, rather than a PCB. | ||||||
| Crumbuino-Nano [145] | chip45.com [146] | ATmega328 | The Crumbuino-Nano is a low-cost module comparable to the Arduino-Nano and can be used as Arduino-Nano in the Arduino-IDE. The Arduino bootloader is preloaded, hence the module is ready-to-use. The documentation shows the pin mapping of Arduino-naming to module pinout. | |||||
| Crumbuino-Mega [147] | chip45.com [146] | ATmega2560 [25] | The Crumbuino-Mega is a low-cost module comparable to the Arduino-Mega 2560 and can be used as Arduino-Mega 2560 in the Arduino-IDE. The Arduino bootloader is preloaded, hence the module is ready-to-use. The documentation shows the pin mapping of Arduino-naming to module pinout. | |||||
| Cuteduino | Cytron Technologies |
ATtiny85 | Cuteduino Features:
| |||||
| Digispark [148] | Digistump [149] | ATTiny85 |  Built-in USB plug. Requires special version of the Arduino IDE. | |||||
| DragonFly [150] | ATmega1280 [52] | A compact board with Molex connectors, aimed at environments where vibration could be an issue.
DragonFly features the ATmega1280 and have all 86 I/O lines pinned out to connectors. | ||||||
| Femtoduino [151] | Femtoduino [152] | ATmega328P-MU |  An ultra-small (20.7x15.2 mm) Arduino compatible board designed by Fabio Varesano. Femtoduino is currently the smallest Arduino compatible board available. | |||||
| Freeduino USB Mega 2560 [153] | Bhasha Technologies [154] |
ATmega2560 [25] |  Freeduino USB Mega 2560 is a cost-effective and 100% pin and software compatible to the popular Arduino Mega 2560. Uses through hole components and has male headers. | |||||
| Freeduino Lite v2 [155] | Bhasha Technologies [154] |
ATmega8/ 168/328 |
Freeduino Lite v2 is a low cost, Freeduino with no USB and Serial port. Needs FTDI USB Cable or FTDI Breakout board for programming. Uses through hole components and has male headers. | |||||
| Freeduino Serial [156] | Bhasha Technologies [154] |
ATmega8/ 168/328 |
Freeduino Serial is a low cost Freeduino board with serial DB9 connector.
Uses MAX232 Chip for Serial connectivty. | |||||
| Freeduino NANO [152] | Bhasha Technologies [154] |
ATmega328 |  Freeduino Nano is a low cost Arduino Nano compatible board with mini USB connector using SMD components Freeduino Nano. | |||||
| iDuino [151] | A USB board for breadboarding, manufactured and sold as a kit by Fundamental Logic. | |||||||
| IMUduino [157] | Femtoduino.com [158] | ATMega32u4 | The world's first wireless 3D position, inertia, and orientation beacon. Designed in the San Francisco bay area, this board provides a 10-DoF IMU with on-board ATMega32u4 chip (the same as the Arduino Leonardo). | |||||
| JeeNode [159] | JeeLabs [160] | ATmega328P |  Low-cost, low-size, radio-enabled Arduino-compatible board running at 3.3V. Inspired by the Modern Device RBBB (above) with a HopeRF RFM12B wireless module and a modular I/O design supporting a wide range of interfaces. [161] | |||||
| LCDuino [162] | Geppetto Electronics |
ATmega328P | A combination of an ATMega328P and an i2c based RGB backlit LCD interface (software compatible with the Adafruit RGB LCD shield), along with a USB serial programming interface done as a "backpack" module for the LCD. | |||||
| LEDuino [163] | A board with enhanced I²C, DCC decoder and CAN-Bus interfaces.
Manufactured using surface mount and sold assembled by Siliconrailway. | |||||||
| Moteino [164] | LowPowerLab [165] | ATmega328P |  An SD-card size wireless-enabled breadboard friendly Arduino compatible board running at 16MHz/3.3V. It can mate with either an RFM12B or RFM69W/HW/CW transceiver from HopeRF, allowing very low cost wireless communication (also available without a transceiver). | |||||
| NavSpark [167] | SkyTraq [168] | Venus822 (Leon3 SPARC V8 compatible, @100MHz 32-bit RISC) | The modified Arduino IDE allows the compiled user sketch to be uploaded onto
the processor either with or without the proprietary GNSS software. NavSpark has 17 GPIO pins, which include two UARTs, 1 I²CSPI, 1 PWM, and a trigger. The first UART is usually used by the GNSS software to output NMEA 0183 data, although this can be disabled. This UART communicates over USB through a PL2303 serial converter and the transmit output is also made available on a pin. A 1 pulse per second signal is produced on a dedicated pin when a valid fix has been made. There is a GPS-only version, a combined GPS/GLONASS version, and a GPS/Beidou version. An adaptor board adds a JST connector for a Li-ion battery, a charger for the battery, and a microSD card slot connected to the SPI pins. | |||||
| NB1A [169] | An Arduino-compatible board that includes a battery backed up real-time clock and a four channel DAC.
Most Arduino-compatible boards require an additional shield for these resources. | |||||||
| NB2A [170] | Sanguino-compatible board that includes a battery backed up real-time clock and a two channel DAC.
Sanguino's feature the ATmega644P, which has additional memory, I/O lines and a second UART. | |||||||
| Nymph [171] | ATmega328P | A compact board with Molex connectors, aimed at environments where vibration could be an issue. | ||||||
| Oak Micros om328p [172] | An Arduino Duemilanove compacted down to a breadboardable device (36mm x 18mm) that can be inserted
into a standard 600mil 28-pin socket, with USB capability, ATmega328P, and 6 onboard LEDs. | |||||||
| OpenTag [173] | Loggerhead Instruments |
ATmega328p | 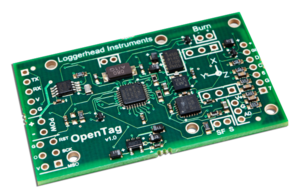  Arduino-compatible microSD motion datalogging board with accelerometer, magnetometer, gyroscope, pressure, temperature and real-time clock. | |||||
| Paperduino [174] | ATmega168 | An ultra low-cost Arduino compatible, built on a printed paper and cardboard substrate, rather than a PCB. | ||||||
| Photon [175] | Particle | STM32F205 [176] (ARM Cortex-M3) |
An ARM-based Wi-Fi development kit with a Broadcom BCM43362 Wi-Fi chip supporting 802.11b/g/n. | |||||
| PicoDuino [177] | Peter Misenko | ATTiny85 | 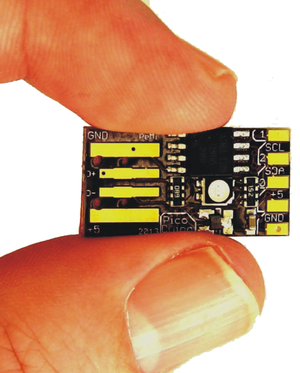
| |||||
| Pro Micro [178] | Sparkfun and clones | ATmega32u4 | A popular low-cost compact Arduino-compatible board. Available in 3.3v and 5v versions. | |||||
| Rainbowduino [179] | . | An Arduino-compatible board designed specifically for driving LEDs.
It is generally used to drive an 8x8 RGB LED matrix using row scanning, but it can be used for other things. | ||||||
| Sanguino [180] | ATmega644 |  An open source enhanced Arduino-compatible board that uses an ATMega644P instead of an ATmega168. This provides 64kB of flash, 4kB of RAM and 32 general I/O pins in a 40 pin DIP device. It was developed with the RepRap Project in mind. | ||||||
| Seeeduino Mega [181] | SeeedStudio | ATmega2560 [25] | Arduino Mega compatible board with 16 extra I/O pins and the same a board size as the Arduino Uno.
As with the Arduino Mega, most shields that were designed for the Duemilanove, Diecimila, or Uno will fit, but a few shields will not fit because of interference with the extra pins. | |||||
| Sippino [182] | SpikenzieLabs | . | A miniature Arduino compatible board with all of the digital and analog I/O pins brought out into a single line of pins (SIP).
Available as a kit, intended for use with a solderless breadboard. | |||||
| SODAQ Mbili [183] | SODAQ | ATmega1284P |  The Raspberry Pi-sized SODAQ board is built for Solar Powered Data Acquisition.
It is fitted with a Lipo charge controller and 12 Grove sockets for plug and play prototyping.
It runs at 3.3V and 8MHz. It also comes with a DS3231 Real Time Clock and 16 Mbit serial flash for data logging.
Its "bee" socket can use a range of different modules, like Xbee, RFbee, Bluetoothbee and GPRSbee to make the board communicate.
The latest version has the powerful ATmega1284P microcontroller with 128KB program space and 16KB RAM and is still Arduino IDE compatible.
| |||||
| Sparrow [184] | Open Home Automation |
ATMega328P | Arduino compatible board designed specifically for RF mesh network experiments.
It features 10 I/Os, a 10 pin ISP programming connector, a connector for a standard LCD display (in 4 bit mode) and a connector for a 2.4GHz RF module. | |||||
| Spider Controller [185] | . | Arduino Mega compatible board designed specifically for robots requiring large numbers of servos.
A built in 3A switchmode power supply allows servos to plug directly into the board. Pin spacing allows making custom shields from standard prototype board. | ||||||
| Stickduino [186] | . | Similar to a USB key | ||||||
| Teensy 2.0 [187] | PJRC | Atmega32U4 8-bit AVR [188] |
16 MHz |  Boards from PJRC.com that run most Arduino sketches using the Teensyduino software add-on to the Arduino IDE. | ||||
| Teensy 2.0++ [189] | PJRC | AT90USB1286 8-bit AVR [188] |
16 MHz |  A slightly more powerful version of the Teensy 2.0. It has 46 I/O pins; 8KB RAM; 128KB of flash; 10-bit ADC; UART, SPI, I²C, I²S, Touch and other I/O capability. | ||||
| Teensy 3.0 [190] | PJRC | MK20DX128 32-bit ARM (Cortex-M4) [188] |
48 MHz | A very small board based on the Freescale MK20DX128VLH5 CPU. It has 34 I/O pins; 16KB RAM; 128KB of flash;
16-bit ADC; 3xUARTs, SPI, I²C, I²S, Touch and other I/O capability. Version 3.0 is not recommended for new designs. | ||||
| Teensy 3.1/3.2 [191] | PJRC | MK20DX256 32-bit ARM (Cortex-M4) [188] | 72 MHz | Same form factor as Teensy 3.0. Based on the Freescale MK20DX256VLH7 CPU. It has 34 I/O pins; 64KB RAM;
256kB of flash; 2x16-bit ADC; 12-bit DAC; 3xUARTs, SPI, 2xI²C, I²S, CAN Bus, Touch and other I/O capability. All digital pins are 5 volt tolerant. Teensy 3.2 adds a more powerful 3.3 volt regulator, with the ability to directly power ESP8266 Wi-Fi, WIZ820io Ethernet and other power-hungry 3.3V add-on boards. | ||||
| Teensy LC [192] | PJRC | MKL26Z64VFT4 ARM (Cortex-M0+) [192] |
48 MHz | A lower cost version of the Teensy 3.1/3.2. It has 27 I/O pins; 64kB of flash; 12-bit DAC; 3xUARTs, 2xSPI, 2xI²C, I²S, Touch and other I/O capability. I/O pins are not 5V tolerant. No FIFOs on Serial 1 and Serial2. Fewer hardware timers. | ||||
| TinyDuino [193] | TinyCircuits [194] | ATmega328p | 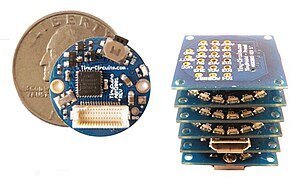 A fully capable Arduino platform smaller than a quarter, yet with all the power and functionality of the Arduino Uno board, including stackable shield support. The TinyDuino also support an option coin cell holder and has many expansion shields available. | |||||
| TinyLily [195] | TinyCircuits [194] | ATmega328p |  A fully capable Arduino platform smaller than a dime, designed for e-textiles. Includes large sewtabs and a header for a USB adapter for communication and programming. | |||||
| Trinket [196] | Adafruit | ATTiny85 | Requires updates to Arduino IDE (or download special version) and driver under Windows. Includes regulator for battery power away from PC. Very low cost. | |||||
| Wireless Widget [197] | . | A compact (35mm x 70mm), low voltage, battery powered Arduino-compatible board with onboard wireless capable of ranges up to 120m. The Wireless Widget was designed for both portable and low cost Wireless sensor network applications. | ||||||
| Whisper Node AVR [198] | Wisen - Talk² | ATmega328p |  A real ultra-low power board, capable of running of a single AA. The board counts with an efficient step-up regulator (MCP16251) and can be powered from 0.9V. The Whisper Node has a built-in RFM69 long-range sub-GHz radio and 4Mbit Flash memory. The board can also run from a standard power supply and use the battery as backup. Additionally it can be upgraded to include a RTC chip or a high-voltage LDO. On field tests the Whisper Node was able to communicate on distances over 1 km line-of-sight and can run for years on battery, making a great platform for remote sensing and IoT applications. | |||||
| ZB1 [199] | . | An Arduino-compatible board that includes a Zigbee radio (XBee). The ZB1 can be powered by USB, a wall adapter or an external battery source. It is designed for low-cost Wireless sensor network applications. | ||||||
| SunDuino2 [96] | ATmega16/ 32/324/644 |
An open source enhanced Arduino-compatible board that uses an ATmega16 /32 /324/ 644 instead of an ATmega168. This provides 16/32/64 kB of flash, and 32 general I/O pins in a 40 pin DIP device. | ||||||
| OpenEnergyMonitor emonTx [200] | ATmega328 |  An open-source low power wireless (RFM12B) energy monitoring node based on ATmega328 and JeeNode design and uses the Nanode (another Arduino compatible) design for their receiver. [201] | ||||||
| PanStamp [202] | panStamp [202] | ATmega328 | File:PANSTAMP.jpg Small low-power wireless motes and base boards. Communication library, configuration tools and automation applications are available for panStamps. These wireless miniatures can easily be hooked to different cloud data services via Lagarto, [203] an open automation platform developed for panStamps. [202] | |||||
| Microduino [204] [205] | Microduino Studio | ATmega168/ 328/644/1284 |
1" x 1.1" small, stackable, low-cost Arduino-compatible board with a uniformed U-shape 27-pin standard interface. | |||||
| Versalino Uno [206] | Virtuabotix | ATmega328p |  Compact board with pins in two similar layouts "Bus A" and "Bus B". 6 volt input 3.5mm plug power. Programmed with FTDI. | |||||
| LeoStick [207] | Freetronics | ATmega32U4 | Compact version of the Arduino Leonardo (which can be plugged straight into a USB port without a cable) and has a buzzer and a 3-in-1 RGB LED. | |||||
| Wattuino Nanite [208][209] | Watterott electronic | ATtiny85 / ATtiny841 | Very small size and microUSB plug for programming (Micronucleus USB Bootloader). Requires special board package for the Arduino IDE. | |||||
| Wattuino Pro Mini PB [210] | Watterott electronic | ATmega328PB | An Arduino Pro Mini compatible board with the new ATmega328PB. Requires special board package for the Arduino IDE. | |||||
| PIC.duino Net | SlicMicro | PIC18F67J60 | Ethernet or Serial | Pin compatible with Arduino but uses the ethernet enabled PIC microcontroller to connect to the Internet. Allows sending of email, display of javascript enabled webpages, and remote web based access and control from around the world. | ||||
| Leaflabs Maple [211] | LeafLabs [212] | STM32 (ARM Cortex-M3) | 72 MHz | USB |  A 72MHz 32-bit ARM Cortex-M3-based microcontroller (STMicro] STM32F103 [213]) with USB support, compatibility with Arduino shields, and 39 GP I/O pins. Programmable with the Open Source Maple IDE, [214] which is a branch of the Arduino IDE. The Maple IDE includes both an implementation of the Arduino Language, [215] and lower-level native libraries (with support from the libmaple C library). [216] The more up-to-date Arduino_STM32[217] project allows use of the Maple, and other generic STM32 boards in version 1.6.12 of the Arduino IDE. | |||
| Microchip chipKIT Uno32, Max32, WF32, DP32 |
Digilent [218] | PIC32 | USB | 32-bit MIPS-M4K PIC32MX processor boards (40-80MHz). The Arduino libraries have been implemented natively for the PIC32MX and these kits run in a fork of the standard Arduino IDE, MPIDE [219] and are compatible to most shields. [220][221]< ref name="Auto7L-102" /> | ||||
| Microchip chipKIT Wi-Fire | Digilen t[218] | PIC32MZ | 200MHz | USB | 32-bit MIPS-M4K PIC32MZ processor boards (200MHz). The Arduino libraries have been implemented natively for the PIC32MZ and these kits run in a fork of the standard Arduino IDE, MPIDE [219] and are compatible to most shields. [220][221][222] | |||
| Freescale Freedom | Freescale [223] | Kinetis-L (ARM Cortex-M0+) | 48MHz | USB | A 48MHz 32-bit ARM Cortex-M0+ -based microcontroller (Freescale MKL25Z128VLK4 [224]) with USB support, compatibility with Arduino shields and 64 GP I/O pins. Board embeds the new ARM OpenSDA debug and programming interface through USB and is compatible with the majority of the ARM IDE suppliers. | |||
| PRO Family [225] | Coridium [226] | ARM Cortex LPC1114 LPC1751 LPC1756 | 200MHz | USB | Up to 200MHz dual core ARM Cortex-M4F, ARM Cortex-M3 and ARM7TDMI-based shield-compatible boards, programmable in BASIC or C with Sketch support with open source MakeItC utilities. All boards have 5V tolerant I/Os. | |||
| Energia | TI | MSP430 | USB | The Energia project integrates this with the Arduino IDE. | ||||
| Sakura board [227] | Renesas /Wakamatsu Tsusho Co., Ltd | Renesas RX63N | USB | Web compiler with Sketch support, ethernet interface. | ||||
| HiFive1 [228] | SiFive | SiFive E31 32 bit RISC-V | USB |  Uno form factor, 5V and 3.3V, 19 digital I/O (9 PWM), 0 analogue in. 16 MB QSPI flash (execute in place, with 16 KB icache), 16 KB SRAM. Arduino IDE support with 16/256/320 MHz presets and port of Arduino library. Also works with standard C/C++, stdio, gdb from the shell. Hardware multiply (4 cycle) and divide (32 cycle). | ||||
| DAQduino | PICcircuit.com | PIC18F2550 or PIC18F2553 | DAQduino is iCP12 usbStick that built in Arduino form of external ports connection. With these IO ports, user can easily plug in different type of 3rd party Arduino extension boards with direct connection to USB port and SmartDAQ software. Great tool for parallel USB IO control, signals monitoring (6 ch. oscilloscope) and data acquisition. | |||||
| CIKU | Cytron Technologies | PIC18F4550 | 48 MHz | CIKU Features:
| ||||
| Chipino | Howtronics | Microchip PIC16F886-I/SP | Chipino is an electronics prototyping platform based on a Microchip PIC microcontroller. It was designed to use the same footprint and connection scheme as the official Arduino boards to allow Arduino shields to be used with Chipino. | |||||
| Bambino 210 | Microint USA | NXP LPC4330 | Dual core ARM Cortex-M4/M0, 264 KB SRAM, 4 MB Flash, mbed HDK, Arduino-compatible headers. The Bambino 210E has the same features as the 210, but adds a 10/100 Ethernet port, 8MB Flash, microSD socket, and Xbee Socket. | |||||
| Cypress PSoC 4 Pioneer Kit (CY8CKIT-042) | Cypress | Cypress CY8C4245 AXI-483 | The PSoC 4 Pioneer Kit is a development platform enabling users to design with the ARM Cortex-M0 PSoC 4 device family. The kit features the PSoC 4200 device family as the main processor and includes a PSoC 5LP (ARM Cortex-M3 processor) to perform programming and debugging. The kit is supported using PSoC Creator, which is a free IDE for embedded development targeting the PSoC 3/4/5LP device families. In the summer of 2013 Cypress supported the kit with a 100 projects in 100 days campaign on the community forums at Element14. | |||||
| Arduino Shield Compatible Propeller Board [229] | Parallax, Inc. | Parallax Propeller | Based on the Parallax Propeller; interfaces with standard Arduino shields. The Propeller comes with a free IDE called "propeller tool", and an alternative IDE tool is available. [230] | |||||
| Amicus18 [231] | PIC | Amicus18 is an embedded system platform based on PIC architecture (18F25K20). Can be programmed with any programming language, though the Amicus IDE is free and complete. | ||||||
| Cortino [232] | ARM STM32 | Development system for a 32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 -based microcontroller. | ||||||
| Pinguino [233] | PIC | Board based on a PIC microcontroller, with native USB support and compatibility with the Arduino programming language plus an IDE built with Python and sdcc as compiler. | ||||||
| Unduino [234] | PIC | A board based on the dsPIC33FJ 128MC202 microcontroller, with integrated motor control peripherals. | ||||||
| Netduino | ||||||||
| Netduino N2 [235] | Wilderness Labs [235] | Cortex-M3 (ARMv7-M) | 120MHz | Arduino | 69x53mm | USB | 12MHz 32-bit ARM7 microcontroller board with support for the NET Micro Framework. Pin compatible with Arduino shields although drivers are required for some shields. [235] | |
| Netduino N2 Plus [235] | Wilderness Labs [235] | Cortex-M4 ARMv7E-M |
168MHz | Arduino | 69x53mm | USB | 168MHz 32-bit ARM7 microcontroller board with support for the NET Micro Framework. Pin compatible with Arduino shields although drivers are required for some shields. [235] | |
| Netduino N3 [235] | Wilderness Labs [235] | Cortex-M4 (STM32F4) ARMv7E-M |
168MHz | Arduino | 69x53mm | USB | 168MHz 32-bit ARM7 microcontroller board with support for the NET Micro Framework. Pin compatible with Arduino shields although drivers are required for some shields. [235] | |
| Netduino N3 Ethernet [235] | Wilderness Labs [235] | Cortex-M4 (STM32F4) ARMv7E-M |
168MHz | Arduino | 69x53mm | USB | 168MHz 32-bit ARM7 microcontroller board with support for the NET Micro Framework. Pin compatible with Arduino shields although drivers are required for some shields. [235] | |
| Netduino N3 WiFi [235] | Wilderness Labs [235] | Cortex-M4 (STM32F4) ARMv7E-M | 168MHz | Arduino | 69x53mm | USB | 168MHz 32-bit ARM7 microcontroller board with support for the NET Micro Framework. Pin compatible with Arduino shields although drivers are required for some shields. [235] | |
| Vinculo [236] | Vinculum II | FTDI USB development board for the FTDI Vinculum II microcontroller. | ||||||
| FEZ Domino, [237] FEZ Panda, [238] and FEZ Panda II [239] | ARM | 72 MHz | 72MHz 32-bit ARM (GHI Electronics USBizi chips) micro-controller boards with support for the .NET Micro Framework. Pin compatible with Arduino shields, although drivers are required for some shields. [240] | |||||
| TheUno [241] | MyFreescale WebPage [241] |
Freescale S08DZ60 |
Freescale 8-bit S08DZ60 based Arduino Shield Compatible development board. Programmable in C or assembly language using the free CodeWarrior development environment from Freescale, based on Eclipse. Integrated open-source debugging cable for fast prototyping. | |||||
| BigBrother | ||||||||
| BigBrother [241] | MyFreescale WebPage [241] |
Freescale MCF51AC256 |
Freescale 32-bit Coldfire MCF51AC256 based Arduino Shield Compatible development board. | |||||
| BigBrother-USB [241] | MyFreescale WebPage [241] |
Freescale MCF51JM128 |
Freescale 32-bit Coldfire MCF51JM128 based Arduino Shield Compatible development board. | |||||
| Firebird32 [242] | Freescale ColdFire | Freescale 32-bit Coldfire MCF51JM128 based Arduino Shield Compatible development board. Programmable in StickOS BASIC, and C or assembly language using Flexisframework or CodeWarrior with a step-by-step debugger. | ||||||
| Stampduino | Parallax, Inc. | PIC or Parallax SX | Arduino Shield compatible BASIC Stamp 2 board, interfaces with most standard Arduino shields. The BS comes with a free IDE. | |||||
| STM32 Nucleo | STMicro | STM32 Family | Arduino connectors and ST Morpho headers | |||||
| SunDuinoPIC | PIC18F2550 or PIC18F4550 | Microchip PIC Arduino hardware compatible board. Based PINGUINO Project. USB HID Bootloader. | ||||||
| Breeze [243][244] | PIC | Breeze boards are prototyping platforms for 28-pin PIC microcontrollers. They come with a PIC18F25K22 (USB-UART interface) or PIC18F25J50 (direct USB interface), however almost any 28-pin PIC can be used with the platform. | ||||||
| VM2 | Micro-Robotics Ltd. | STM32F103 | 72MHz | VM2 | 52x48mm | Serial | VM2 is a family of single board microcontrollers intended for use in Automation, Instrumentation, Hand Held Devices and Process Control. Programming environment: Venom2 language, VenomIDE development system, Visual Designer. I/O:
| |
See also
References
- ↑ https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoard101
- ↑ "Intel Curie Module: Unleashing Wearable Device Innovation". intel.com. http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/wearables/wearable-soc.html. Retrieved 2015-08-15.
- ↑ https://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardZero
- ↑ "ATSAMD21G18;". Atmel.com. http://www.atmel.com/devices/ATSAMD21G18.aspx. Retrieved 2014-08-12.
- ↑ https://blog.arduino.cc/2015/06/15/arduino-zero-now-available-for-purchase/
- ↑ https://blog.arduino.cc/2014/05/15/meet-arduino-zero/
- ↑ https://blog.arduino.cc/2014/08/01/20-arduino-zero-dev-edition-available-for-beta-testing-join-us/
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardDue". Arduino.cc. https://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardDue. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino to add ARM board this year". The Register. 2011-09-20. https://www.theregister.co.uk/2011/09/20/arduino_goes_arm/. Retrieved September 20, 2011.
- ↑ Jump up to: 10.0 10.1 10.2 "AT91SAM3X8E;". Atmel.com. http://www.atmel.com/devices/SAM3X8E.aspx. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ Jump up to: 11.0 11.1 11.2 "ATmega16U2". Atmel.com. http://www.atmel.com/devices/atmega16u2.aspx. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "SAM3U4E". Atmel.com. http://www.atmel.com/devices/SAM3U4E.aspx. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "atmel.com". atmel.com. http://www.atmel.com/dyn/products/param_table.asp?category_id=163&family_id=605&subfamily_id=2086&OrderBy=part_no&Direction=ASC. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino Blog- Arduino Due is finally here". Arduino.cc. 2012-10-22. https://blog.arduino.cc/2012/10/22/arduino-due-is-finally-here/. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ https://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardYun
- ↑ Jump up to: 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 16.4 16.5 "ATmega32U4". Atmel.com. http://www.atmel.com/devices/atmega32u4.aspx. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ https://blog.arduino.cc/2013/08/21/updating-about-arduino-yun-and-arduino-robot/
- ↑ "Arduino - ArduinoBoardLeonardo". Arduino.cc. https://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardLeonardo. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Arduino Blog- Massimo Introduces Arduino Leonardo". Arduino.cc. 2012-07-23. https://blog.arduino.cc/2012/07/23/massimo-introduces-arduino-leonardo/. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino - ArduinoBoardUno". Arduino.cc. https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardUno. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 21.0 21.1 "ATmega328P". Atmel.com. http://www.atmel.com/devices/atmega328p.aspx. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ Jump up to: 22.0 22.1 22.2 "ATmega8U2". Atmel.com. http://www.atmel.com/devices/atmega8u2.aspx. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ Jump up to: 23.0 23.1 "Arduino Blog- Dinner is Ready". Arduino.cc. 2010-09-24. https://blog.arduino.cc/2010/09/24/dinner-is-ready/. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino - ArduinoBoardMega2560". Arduino.cc. https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardMega2560. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 25.0 25.1 25.2 25.3 25.4 25.5 25.6 25.7 25.8 "ATmega2560". Atmel.com. http://www.atmel.com/devices/atmega2560.aspx. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardEthernet". Arduino.cc. https://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardEthernet. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ Jump up to: 27.0 27.1 27.2 "ATmega328". Atmel.com. http://www.atmel.com/devices/atmega328.aspx. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ Jump up to: 28.0 28.1 "Arduino Blog- Arduino Ethernet, ADK Available for purchase". Arduino.cc. 2011-07-13. https://blog.arduino.cc/2011/07/13/arduino-ethernet-adk-available-for-purchase/. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino - ArduinoEthernetShield". Arduino.cc. https://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoEthernetShield. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 30.0 30.1 "Arduino - ArduinoBoardFio". Arduino.cc. https://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardFio. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Arduino Blog- Arduino FIO presented at Uno Punto Zero". Arduino.cc. 2010-03-18. https://blog.arduino.cc/2010/03/18/arduino-fio-presented-at-uno-punto-zero/. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardNano". Arduino.cc. https://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardNano. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ Jump up to: 33.0 33.1 33.2 33.3 33.4 33.5 33.6 33.7 33.8 "ATmega168". Atmel.com. http://www.atmel.com/devices/atmega168.aspx. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "FT232R". ftdichip.com. http://www.ftdichip.com/Products/ICs/FT232R.htm. Retrieved 2014-08-14.
- ↑ "Arduino Blog - Arduino Nano: all-in-one design for breadboard use". Arduino.cc. 2008-05-15. https://blog.arduino.cc/2008/05/15/arduino-nano-all-in-one-design-for-breadboard-use/. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardLilyPad". Arduino.cc. https://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardLilyPad. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino Blog- LilyPad Arduino and Arduino 0010". Arduino.cc. 2007-10-17. https://blog.arduino.cc/2007/10/17/lilypad-arduino-and-arduino-0010/. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ Jump up to: 38.0 38.1 arduino.cc
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardADK". Arduino.cc. https://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardADK. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardEsplora". Arduino.cc. https://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardEsplora. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardMicro". Arduino.cc. https://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardMicro. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino Blog- New Arduino Micro available". Arduino.cc. 2012-11-08. https://blog.arduino.cc/2012/11/08/new-arduino-micro-available/. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino - ArduinoBoardSerial". Arduino.cc. https://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardSerial. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 44.0 44.1 44.2 44.3 "ATmega8". Atmel.com. http://www.atmel.com/devices/atmega8.aspx. Retrieved 2014-08-14.
- ↑ Jump up to: 45.0 45.1 45.2 45.3 "Arduino - Boards". Arduino.cc. 2009-03-01. https://arduino.cc/en/Main/Boards. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 46.0 46.1 "Arduino - ArduinoBoardBluetooth". Arduino.cc. https://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardBluetooth. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 47.0 47.1 "Arduino Blog- Arduino Diecimila and BT reference designs now available". Arduino.cc. 2007-10-22. https://blog.arduino.cc/2007/10/22/arduino-diecimila-reference-design-now-available/. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardDiecimila". Arduino.cc. https://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardDiecimila. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino - ArduinoBoardDuemilanove". Arduino.cc. https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardDuemilanove. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Arduino Blog- Arduino Duemilanove". Arduino.cc. 2008-10-19. https://blog.arduino.cc/2008/10/19/arduino-duemilanove/. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino - ArduinoBoardMega". Arduino.cc. https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardMega. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 52.0 52.1 "ATmega1280". Atmel.com. http://www.atmel.com/devices/atmega1280.aspx. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino Blog- Arduino Mega: bigger, more powerful, still blue". Arduino.cc. 2009-03-26. https://blog.arduino.cc/2009/03/26/arduino-mega-bigger-more-powerful-still-blue/. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino - ArduinoBoardMega". Arduino.cc. https://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardMega. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardProMini". Arduino.cc. https://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardProMini. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino Blog- Arduino Pro and Pro Mini". Arduino.cc. 2008-08-23. https://blog.arduino.cc/2008/08/23/arduino-pro-and-pro-mini/. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Canaduino uno bone - atmega328p-pu". https://www.universal-solder.com/products/canaduino-uno-bone-full-kit-arduino-uno-r3-compatible-atmega328p-pu.
- ↑ "ST Freeduino 1". http://www.sanjaytechnologies.co.in/products/arduino-products/st-freeduino-1.
- ↑ "GSTduino – Arduino Compatible Special Purpose Board". http://www.greensystemtech.com.
- ↑ "SainSmart UNO". sainsmart.com. http://www.sainsmart.com/wiki/index.php/SainSmart_UNO_ATMEGA328P-PU_ATMEGA8U2_Microcontroller_For_Arduino. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 61.0 61.1 61.2 "SainSmart-Open Hardware Company". sainsmart.com. http://www.sainsmart.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "SainSmart UNO R3". sainsmart.com. http://www.sainsmart.com/sainsmart-uno-r3-atmega328-au-development-board-compatible-with-arduino-uno-r3.html. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "SainSmart Mega 2560". sainsmart.com. http://www.sainsmart.com/wiki/index.php/SainSmart_Mega2560_AVR_ATmega2560_ATMEGA8U2_With_Free_USB_cable. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Tavir-AVR : Bascom, Arduino, Wiring - Program, Forum". Avr.tavir.hu. http://avr.tavir.hu/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "TavIR : Mikrokontroller világ | A gyakorlati tudás tárháza" (in hu). Tavir.hu. http://www.tavir.hu/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Brasuíno". Brasuino.holoscopio.com. http://brasuino.holoscopio.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Holoscópio". Holoscopio.com. 2011-07-18. http://holoscopio.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 68.0 68.1 "Chibiduino2". tiisai.dip.jp. http://tiisai.dip.jp/?page_id=1296. Retrieved 17 Aug 2013.
- ↑ "Arduino - "Cosmo Black Star"". Jt5.ru. http://jt5.ru/arduino/cosmo-black-star/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 70.0 70.1 "JT5 :: инжиниринговая компания специализирующая на разработке и производстве электронных устройств". Jt5.ru. http://jt5.ru/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "CraftDuino / RoboCraft". Robocraft.ru. http://robocraft.ru/blog/RoboCraft/97.html. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "diavolino - evilmadscientist.com". http://www.evilmadscientist.com/article.php/diavolino/.
- ↑ "Electronics - Multiplo Robot Building System". Multiplo.org. http://multiplo.org/make-diy/electronics/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Multiplo Robot Building System". Multiplo.org. http://multiplo.org/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Shop.cqpub.co.jp". Shop.cqpub.co.jp. http://shop.cqpub.co.jp/hanbai/books/12/12551.html. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Platino - Versatile Board for AVR Microcontrollers - Elektor Labs". http://www.elektor-labs.com/platino. Retrieved 2015-11-04.
- ↑ Jump up to: 77.0 77.1 "MaxSerial : Fundamental Logic WebStore, Electronic Kits and Components". Store.fundamentallogic.com. 2010-05-30. http://store.fundamentallogic.com/ecom/index.php?main_page=index&cPath=3. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Fayalab Inc.". http://www.fayalab.com. Retrieved 2016-02-18.
- ↑ "SB-Freeduino". Solarbotics. http://solarbotics.com/products/28920/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Solarbotics". Solarbotics. http://solarbotics.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Freeduino USB complete KIT (Arduino Duemilanove Compatible)". Nkcelectronics.com. http://www.nkcelectronics.com/freeduino-arduino-diecimila-compatible-board-complete-kit.html. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Illuminato::Genesis". Liquidware. http://www.liquidware.com/shop/show/ILLI/Illuminato::Genesis/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "InduinoX (dead link)". http://www.induino.com/wiki/index.php?title=InduinoX. Retrieved August 13, 2011.
- ↑ "Simple Labs - Simplifying Technology". Build.simplelabs.co.in. http://build.simplelabs.co.in/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Vol.27". Otonanokagaku.net. http://otonanokagaku.net/magazine/vol27/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Luigino (IT)". Droids.it. http://www.droids.it/cmsvb4/content.php?262-990.110-1000Pads-Luigino/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Luigino 328 - User Manual". Droids.it. http://www.droids.it/cmsvb4/content.php?279-990.023-Luigino328-User-Manual-EN. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Metaboard – Metalab" (in de). Metalab.at. http://metalab.at/wiki/Metaboard. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Small computers for art and science". Rascal Micro. http://rascalmicro.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Raspduino". Archived from the original on March 31, 2013. https://web.archive.org/web/20130331012625/http://www.bitwizard.nl/wiki/index.php/Raspduino. Retrieved January 23, 2013.
- ↑ "BitWizard". Bitwizard.nl. http://www.bitwizard.nl/catalog/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "DFRduino Romeo-All in one Controller V1.1 (SKU:DFR0004) - Robot Wiki". Dfrobot.com. http://www.dfrobot.com/wiki/index.php?title=DFRduino_Romeo-All_in_one_Controller_V1.1%28SKU:DFR0004%29. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "DFRobot-An - Opensource Robot and Hardware". Dfrobot.com. http://www.dfrobot.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Roboduino for DIY". Curious Inventor. http://www.curiousinventor.com/kits/roboduino/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Seeeduino V3.0 (Atmega 328P): Seeed Studio". Seeedstudio.com. http://www.seeedstudio.com/depot/Seeeduino-V30-Atmega-328P-p-669.html. Retrieved 9 Nov 2014.
- ↑ Jump up to: 96.0 96.1 "SunDUINO Nowy wymiar elektroniki". Sunduino.pl. http://www.sunduino.pl/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Electronic Components for Arduino - TwentyTen (Arduino Compatible)". Freetronics. http://www.freetronics.com/products/twentyten. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Electronic Components for Arduino - Welcome". Freetronics. http://www.freetronics.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Volksduino: complete low-cost Arduino clone". Appliedplatonics.com. http://appliedplatonics.com/volksduino/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 100.0 100.1 "Applied Platonics". Applied Platonics. http://appliedplatonics.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Wise time with Arduino". Timewitharduino.blogspot.com. http://timewitharduino.blogspot.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 102.0 102.1 "YourDuino". YourDuino. http://yourduino.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "YourDuinoRobo1 (Upgraded Arduino Compatible)". Arduino-direct.com. http://yourduino.com/sunshop2/index.php?l=product_detail&p=225. Retrieved 2014-09-23.
- ↑ "geekstudio.co.za". GeekStudio. http://www.geekstudio.co.za/products/zardino/.
- ↑ "Zigduino r1 - Logos Electromechanical". Logos-electro.com. http://www.logos-electro.com/zigduino/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Products & Services - Logos Electromechanical". Logos-electro.com. 1999-02-22. http://www.logos-electro.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ http://www.freetronics.com/collections/arduino/products/etherten
- ↑ http://www.freetronics.com/collections/arduino/products/ethermega-arduino-mega-2560-compatible-with-onboard-ethernet
- ↑ http://www.freetronics.com/collections/arduino/products/usbdroid
- ↑ http://www.freetronics.com/collections/arduino/products/eleven
- ↑ http://www.freetronics.com/collections/arduino/products/kitten
- ↑ CATkit
- ↑ http://www.freetronics.com/collections/arduino/products/etherdue-arduino-due-compatible-with-onboard-ethernet
- ↑ http://www.elechouse.com/elechouse/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=72_73&products_id=2212
- ↑ http://www.hitex.co.uk/index.php?id=3650
- ↑ "Io:duino". Railstars. http://railstars.com/hardware/io/io-duino/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "DFRobotShop Rover V2 - Arduino Compatible Tracked Robot (Basic Kit)". RobotShop. http://www.robotshop.com/dfrobotshop-rover-tracked-robot-basic-kit.html. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Mindsets online". Mindsets online. 2007-03-01. http://www.mindsetsonline.co.uk/product_info.php?products_id=1009809. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Mindsets online.co.uk". Mindsets online.co.uk. 2007-03-01. http://www.mindsetsonline.co.uk/about_us.php. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Mindsets online.co.uk". Mindsets online.co.uk. http://www.mindsetsonline.co.uk/images/Faraduino.pdf.
- ↑ "Bump and Reverse Robot Kit (Faraduino)". Mindsets online. 2007-03-01. http://www.mindsetsonline.co.uk/product_info.php?products_id=1009885. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Faraconnect Shield (Faraduino)". Mindsets online. 2007-03-01. http://www.mindsetsonline.co.uk/product_info.php?products_id=1009886. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Motoruino - GuiBot". Guibot.pt. http://www.guibot.pt/motoruino/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Arduino based Alternator Regulator". http://arduinoalternatorregulator.blogspot.com/.
- ↑ Jump up to: 125.0 125.1 "ArduPilot (Legacy) main page". DIY Drones. 2009-01-21. http://diydrones.com/profiles/blogs/ardupilot-main-page/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Flyduino - Multirotor, Multicopter Teile & Zubehör für Quadrocopter, Hexacopter, Octocopter - Motore, Rahmen, FCs & ESCs". Flyduino.net. http://flyduino.net/Flyduino-MEGA-Flight-Controller-CPU-Board_1/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Arduino совместимая платформа "Колибри" с RF радиомодулем 868Mhz :: платы Arduino". Jt5.ru. 2012-03-30. http://jt5.ru/arduino/colibri/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ http://www.freetronics.com/collections/arduino/products/arduphone-arduino-compatible-cellphone
- ↑ "Archived copy". http://wtfduino.co.uk/.
- ↑ http://tah.io
- ↑ http://revealinghour.in
- ↑ Jump up to: 132.0 132.1 132.2 "Controllino". http://controllino.biz/. Retrieved 19 July 2016.
- ↑ "FA-DUINO-12RA (INDUSTRIAL ARDUINO)". http://www.comfiletech.com/new-products-for-2014/fa-duino-12ra-industrial-arduino/. Retrieved 19 July 2016.
- ↑ "ARDBOX". http://www.industrialshields.com/open-source/plc-compacto/. Retrieved 19 July 2016.
- ↑ "Industruino". https://industruino.com. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- ↑ "iono". https://sferalabs.cc/iono.
- ↑ "Ardweeny". Solarbotics. http://www.solarbotics.com/products/kardw/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Banguino". Dimitech. http://dimitech.com/products.php. Retrieved 14 Jun 2014.
- ↑ "аналог Arduino, но другой". Blockduino. http://blockduino.org/index.htm. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Каталог блоков от BlockDuino". Blockduino.org. http://blockduino.org/bd_blocklist.htm. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Boarduino - Breadboard-compatible Arduino Clone". Ladyada.net. 2011-08-15. http://www.ladyada.net/make/boarduino/index.html. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Breaduino: the all-breadboard Arduino clone". Appliedplatonics.com. http://appliedplatonics.com/breaduino/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Croduino Basic 5x3cm Arduino Duemilanove compatible board". e-radionica.com. https://e-radionica.com/en/croduino/croduino-boards.html. Retrieved 2016-01-15.
- ↑ chip45.com - Crumbuino-Nano
- ↑ chip45.com - Crumbuino-Mega
- ↑ Jump up to: 146.0 146.1 "Microcontroller Modules, Boards, Tools and Accessories for Atmel AVR ATmega Xmega Processors". Chip45.com. http://www.chip45.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Electronics for Hobbyists". Circuit Monkey. http://www.circuitmonkey.com/index.php?name=Catalog&mode=i&item=000106. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Digispark USB Development Board". http://digistump.com/products/1. Retrieved 2014-06-05.
- ↑ "Digistump". http://digistump.com/. Retrieved 2014-06-05.
- ↑ "DragonFly - ATmega1280 Arduino Bundle - Circuit Monkey". Circuitmonkey.com. http://www.circuitmonkey.com/?name=Catalog&mode=i&item=000110. Retrieved 2014-11-04.
- ↑ Jump up to: 151.0 151.1 "iDuino Complete Kit iDuino-3-kit: Fundamental Logic WebStore, Electronic Kits and Components". Spiffie.org. 2010-05-30. http://www.spiffie.org/store/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=2&products_id=10. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 152.0 152.1 "Smallest Arduino". Femtoduino. 2012-04-21. http://femtoduino.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "freeduino lite v2". Bhashatech.com. http://www.bhashatech.com/boards/70-freeduino-lite2.html. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 154.0 154.1 154.2 154.3 "Bhasha Technologies". Bhashatech.com. http://www.bhashatech.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Freeduino Serial india". Bhashatech.com. 2009-08-23. http://www.bhashatech.com/boards/10-freeduino-serial.html. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Femtoduino: an ultrasmall (20.7x15.2 mm) libre Arduino compatible board". Varesano.net. http://www.varesano.net/projects/hardware/Femtoduino/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ [1], specifications
- ↑ [2], Femtoduino.com website
- ↑ "JN - JeeLabs Hardware - JeeLabs". Jeelabs.net. http://jeelabs.net/projects/hardware/wiki/JN6. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "JeeLabs - Computing stuff tied to the physical world". JeeLabs. 2013-01-19. http://jeelabs.org/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Wiki - JeeLabs Hardware - JeeLabs". Jeelabs.net. http://jeelabs.net/projects/hardware/wiki/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ [3], LCDuino blog
- ↑ "Silicon Railway. Small, powerful, and versatile at a reasonable cost". Siliconrailway.com. http://www.siliconrailway.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ lowpowerlab.com, All about Moteino
- ↑ lowpowerlab.com
- ↑ [4] DualOptiboot
- ↑ "SkyTraq". http://www.skytraq.com.tw/. Retrieved 2014-06-05.
- ↑ "Wiblocks - NB1A - ATmega328 + DAC + RTC". Wiblocks.luciani.org. http://wiblocks.luciani.org/NB1/NB1A-index.html. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Wiblocks - NB2 System". Wiblocks.luciani.org. http://wiblocks.luciani.org/NB2/index.html. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Electronics for Hobbyists". Circuit Monkey. http://www.circuitmonkey.com/index.php?name=Catalog&mode=i&item=000013. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "om328p". Oak Micros. Archived from the original on 2012-10-23. https://web.archive.org/web/20121023123639/http://oakmicros.com/content/om328p.html. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "OpenTag Board". Loggerhead Instruments. http://loggerhead.com/products/opentag-board. Retrieved 9 Nov 2014.
- ↑ "Guilherme Martins : PAPERduino's design". Lab.guilhermemartins.net. http://lab.guilhermemartins.net/2009/05/06/paperduino-prints/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Particle Store". Particle. https://store.particle.io/?product=particle-photon. Retrieved 2015-09-28.
- ↑ "STM32F2x5". st.com. http://www.st.com/web/en/catalog/mmc/FM141/SC1169/SS1575/LN1433. Retrieved 2015-09-28.
- ↑ "Picoduino". Peter Misenko. https://www.tindie.com/products/bobricius/picoduino/. Retrieved 4 June 2014.
- ↑ https://www.sparkfun.com/products/12640
- ↑ "Rainbowduino LED driver platform - Atmega 328 Rainbowduino LED driver platform : Seeed Studio Bazaar, Boost ideas, extend the reach". Seeedstudio.com. http://www.seeedstudio.com/depot/rainbowduino-led-driver-platform-plug-and-shine-p-371.html. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "What Is Sanguino?". Sanguino.cc. http://sanguino.cc/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Seeeduino Mega : Seeed Studio Bazaar, Boost ideas, extend the reach". Seeedstudio.com. http://www.seeedstudio.com/depot/seeeduino-mega-p-717.html?cPath=80. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Sippino". SpikenzieLabs. 2011. http://www.spikenzielabs.com/SpikenzieLaba/sippino.html. Retrieved 9 Nov 2014.
- ↑ "SODAQ board". www.sodaq.net. http://www.sodaq.net. Retrieved 2 Oct 2013.
- ↑ "Sparrow prototyping board". open-homeautomation.com. http://www.open-homeautomation.com/projects/sparrow/. Retrieved 2013-05-13.
- ↑ "Red Back Spider robot controller - Let's Make Robots". Letsmakerobots.com. http://letsmakerobots.com/node/26054. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "StickDuino - USB Stick Sized Arduino Clone". Spiffie.org. http://spiffie.org/kits/stickduino/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ [5] PJRC Teensy 2.0
- ↑ Jump up to: 188.0 188.1 188.2 188.3 [6] PJRC teensy variants
- ↑ [7] PJRC Teensy 2.0++
- ↑ [8], PRJC Teensy 3.0
- ↑ [9] PJRC Teensy 3.1/3.2
- ↑ Jump up to: 192.0 192.1 TeensyLC
- ↑ "TinyDuino". TinyCircuits. http://tiny-circuits.com/products/tinyduino/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 194.0 194.1 "A Maker of Tiny Open Source Circuits". TinyCircuits. http://tiny-circuits.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "TinyLily". TinyCircuits. http://tiny-circuits.com/products/tinylily/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ https://learn.adafruit.com/introducing-trinket
- ↑ "strobit - Strobit Wireless Widget Open Hardware Project - Google Project Hosting". https://code.google.com/p/strobit. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Product: Talk² Whisper Node – AVR" (in en-US). Talk² by Wisen. 2016-02-03. https://talk2.wisen.com.au/product-talk2-whisper-node-avr/.
- ↑ "Wiblocks - ZB1 System". Wiblocks.luciani.org. http://wiblocks.luciani.org/ZB1/index.html. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "emonTx". OpenEnergyMonitor. http://openenergymonitor.org/emon/emontx. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Project:Nanode - London Hackspace". Wiki.london.hackspace.org.uk. http://wiki.london.hackspace.org.uk/view/Project:Nanode. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 202.0 202.1 202.2 "Wireless Arduino-compatible miniatures". panStamp. http://www.panstamp.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Lagarto: open automation platform". https://code.google.com/p/panstamp/wiki/lagarto/. Retrieved March 17, 2015.
- ↑ "Microduino Wiki(English)". www.microduino.net. http://wiki.microduino.cc. Retrieved 10 Oct 2013.
- ↑ "Microduino Wiki(中文)". www.microduino.net. http://wiki.microduino.net. Retrieved 10 Oct 2013.
- ↑ Versalino-Uno
- ↑ http://www.freetronics.com/collections/arduino/products/leostick
- ↑ https://github.com/watterott/wattuino#wattuino-nanite-85
- ↑ https://github.com/watterott/wattuino#wattuino-nanite-841
- ↑ https://github.com/watterott/wattuino#wattuino-pro-mini-pb
- ↑ "leaflabs.com". leaflabs.com. http://leaflabs.com/devices/maple/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "leaflabs.com". leaflabs.com. http://leaflabs.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ st.com
- ↑ "leaflabs/maple-ide · GitHub". Github.com. https://github.com/leaflabs/maple-ide. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Arduino - Reference". Arduino.cc. https://arduino.cc/en/Reference/HomePage. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "leaflabs/libmaple · GitHub". Github.com. https://github.com/leaflabs/libmaple. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ https://github.com/rogerclarkmelbourne/Arduino_STM32
- ↑ Jump up to: 218.0 218.1 "Digital Design Engineer's Source". Digilent Inc.. http://www.digilentinc.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 219.0 219.1 "chipKIT32/chipKIT32-MAX · GitHub". Github.com. https://github.com/chipKIT32/chipKIT32-MAX. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 220.0 220.1 "Digital Design Engineer's Source". Digilent Inc.. http://www.digilentinc.com/Products/Detail.cfm?NavPath=2,719,896&Prod=CHIPKIT-UNO32. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 221.0 221.1 "Digital Design Engineer's Source". Digilent Inc.. http://www.digilentinc.com/Products/Detail.cfm?NavPath=2,719,895&Prod=CHIPKIT-MAX32. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "chipKIT Uno32: first impressions and benchmarks". Hackaday.com. 2011-05-27. http://hackaday.com/2011/05/27/chipkit-uno32-first-impressions-and-benchmarks/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Welcome to Freescale - Freescale Semiconductor". Freescale.com. http://www.freescale.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "KL2 Product Summary Page". Freescale.com. http://www.freescale.com/webapp/sps/site/prod_summary.jsp?code=KL2&webpageId=133113337965471295E3EC&nodeId=01624698C9E3EC&fromPage=tax. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Coridium". Coridiumcorp.com. http://www.coridiumcorp.com/prod-family2.html. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Coridium". Coridiumcorp.com. http://www.coridiumcorp.com/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Sakura board homepage". Gadget Renesas project. http://sakuraboard.net/index_en.html. Retrieved 2013-10-28.
- ↑ "SiFive - HiFive1". https://www.sifive.com/products/hifive1/.
- ↑ "propellerpowered.com". http://propellerpowered.com/?p=197.
- ↑ "QuickStart 1: Comparison of Programming Tools". Parallax Semiconductor. Archived from the original on 2013-05-22. https://web.archive.org/web/20130522114224/http://www.parallaxsemiconductor.com/quickstart1. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Introducing Amicus18 Beginner Guides". Digital-diy.com. 2010-06-09. http://digital-diy.com/home/amicus18/beginner-guides/195-introducing-the-amicus18.html. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Bugblat Cortino". Bugblat.com. 2012-01-04. http://www.bugblat.com/products/cor.html. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "PINGUINO Project". Hackinglab.org. 2010-08-26. http://www.hackinglab.org/pinguino/index.html. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "unduino.com". http://www.unduino.com/.
- ↑ Jump up to: 235.00 235.01 235.02 235.03 235.04 235.05 235.06 235.07 235.08 235.09 235.10 235.11 235.12 235.13 235.14 "Overview". Netduino. http://netduino.com/netduino/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Development Modules". Ftdichip.com. http://www.ftdichip.com/Products/Modules/DevelopmentModules.htm#Vinculo. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "FEZ Domino". GHI Electronics. http://www.ghielectronics.com/catalog/product/133/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "FEZ Panda". GHI Electronics. http://www.ghielectronics.com/catalog/product/135/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "FEZ Panda II - FEZ Cerbuino Bee". GHI Electronics. http://www.ghielectronics.com/catalog/product/256/. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Comparison". http://tinyclr.com/compare/. Retrieved August 13, 2011.
- ↑ Jump up to: 241.0 241.1 241.2 241.3 241.4 241.5 "MyFreescaleWebPage". MyFreescaleWebPage. http://myfreescalewebpage.free.fr. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ firebird32.com
- ↑ Breeze Boards Dizzy Enterprises website
- ↑ Arduino clone with mikroBUS socket mikroElektronika news article
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "Arduino" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "Auto7L-52" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "Auto7L-54" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "Auto7L-55" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "Auto7L-107" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "??" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "?" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
<ref> tag with name "..." defined in <references> is not used in prior text.Further reading
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||